Step 8 Regulatory databases
Here we used the Interferome db and TTSMI (Triplex Target DNA Site Mapping and Integration). The Interferome db - users guide has the link broken (PDF not found). The parameters are:
- Interferon Type: (ALL) subtype: (ALL)
- Treatment Concentration: Any Treatment Time: Any
- In Vivo / In Vitro: All Species: ALL
- System: (Cell or tissues): ALL
- Sample Types: Any (Normal AND Abnormal)
- Fold Change option - Up: 2.0 Down: 2.0 (The Fold Change value must be greater or equal to 1)
- Gene Symbol List: ACE, ACE2
The output shows several options: Search Conditions, Gene Summary, Experiment Data, Ontology Analysis, TF Analysis (provided by Transfac database), Chromosome, IFN Type, and Basal Expression:
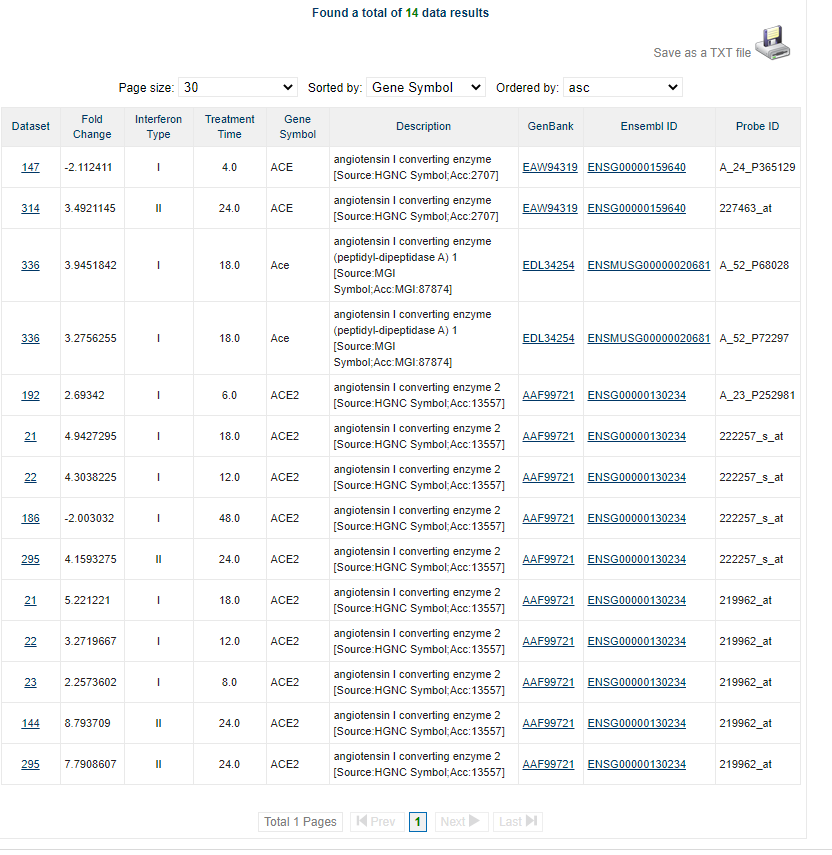
Here the database provides the information about treatment time, interferon types, experiment design and the enrichment values of the transcripts.
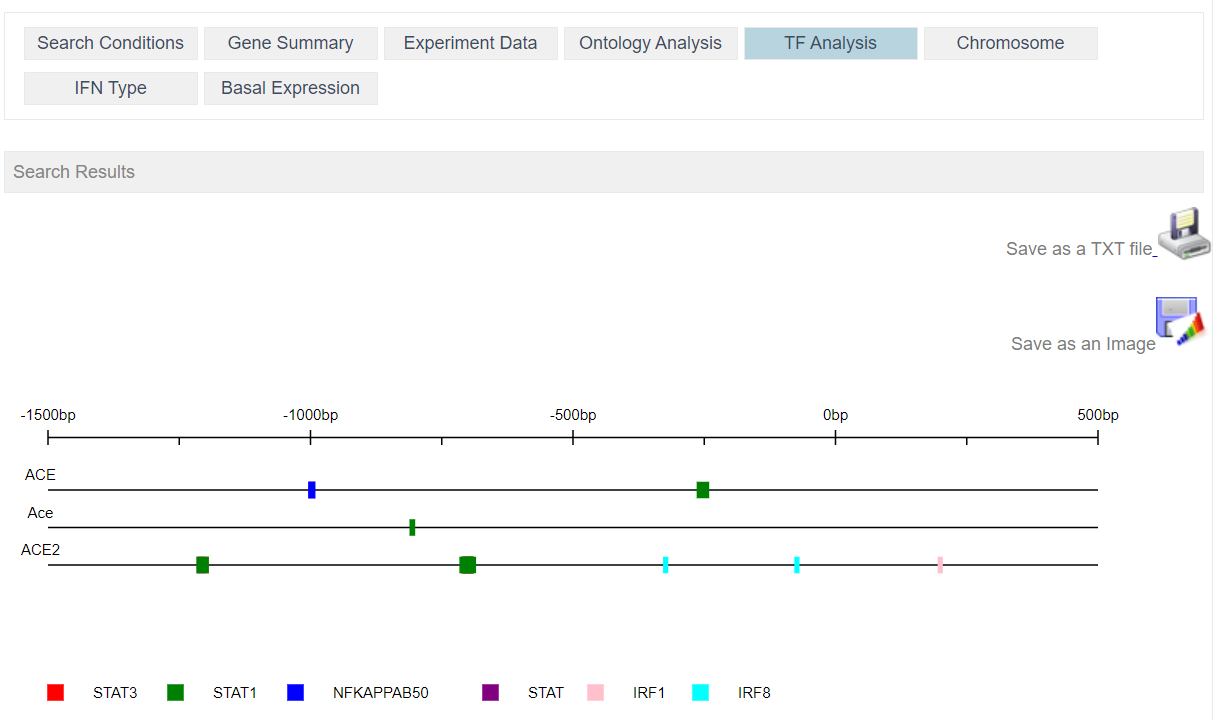
Transcription Factor provided by TRANSFAC database
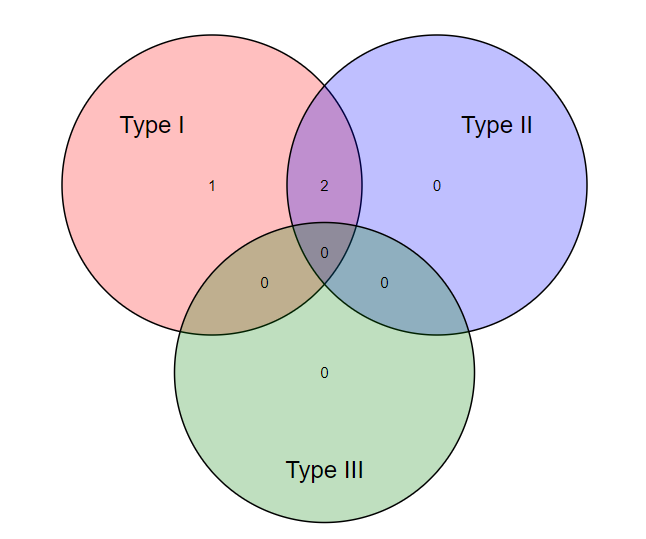
Interferon type: The Venn diagram shows the number of genes regulated by one or more IFN types (Type I, II, or III). It should be noted that there are far more datasets for genes regulated by IFN type I than for types II or III. This imbalance introduces the risk of false-negative and bias for the under-represented types II and III; caution is therefore encouraged in interpreting low or negative results from these types. The location of transcription factors is shown for each of the genes from the region spanning -1500bp to + 500 bp from the start site. Each colored box represents a specific transcription factor, the key for which is provided below the graphic. The user can move the cursor over the transcription factor’s colored box to reveal the TRANSFAC predicted match between the transcription factor and its binding site.
TTSMI (TTS Mapping and Integration) database allows the user to (i) search of the Triplex Target Site (TTS) using several search terms including genomic location, gene ID, NCBI RefSeq ID, TTS ID, gene symbol, and gene description keywords, (ii) interactive filter of the TTS co-localized with several other gene regulatory sequences, (iii) explore a dynamic combination of structural and functional annotations of specific TTS, and (iv) view of the TTS simultaneously with diverse annotation tracks via UCSC genome browser link. The user can quickly search and filter the TTS candidates from the largest collection of unique TTS locations. In terms of finding therapeutic targets, the specificity of TTS is the most important factor in controlling off-target effects.
Search by ACE2 with all default parameters, and the website did not return any results.